题目描述
给你两个非空链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例 1:
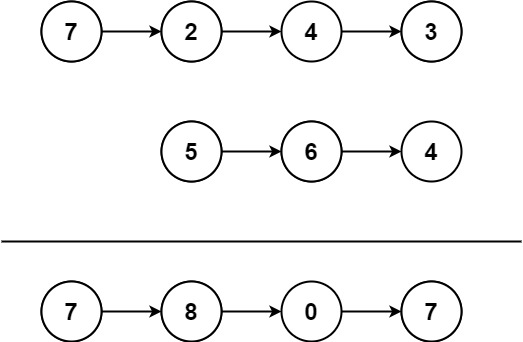
输入:l1 = [7, 2, 4, 3], l2 = [5, 6, 4]
输出:[7, 8, 0, 7]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [2, 4, 3], l2 = [5, 6, 4]
输出:[8, 0, 7]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 链表的长度范围为
[1, 100]
0 <= node.val <= 9- 输入数据保证链表代表的数字无前导
0
栈辅助法
核心思路
利用栈的 后进先出 特性实现逆序处理:
- 遍历两个链表,将节点值分别压入两个栈。
- 同时弹出栈顶元素进行相加,处理进位。
- 使用头插法构建结果链表。
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode resultHead = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int num1 = stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop();
int num2 = stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop();
int sum = num1 + num2 + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
int digit = sum % 10;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(digit);
newNode.next = resultHead;
resultHead = newNode;
}
return resultHead;
}
|
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(max(m, n)),其中 m 和 n 分别为两个链表的长度。
- 空间复杂度:
O(m + n),用于存储两个栈。
链表反转法
核心思路
通过反转链表实现低位对齐:
- 反转两个输入链表。
- 按照两数相加I的方法计算(低位对齐)
- 反转结果链表得到最终答案
参考:
两数相加 I | 笑话人生
反转链表的指针操作与递归实现(LeetCode 206)| 笑话人生
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
l1 = reverseList(l1);
l2 = reverseList(l2);
ListNode l3 = addTwo(l1, l2);
return reverseList(l3);
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
private ListNode addTwo(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int x = (l1 != null) ? l1.val : 0;
int y = (l2 != null) ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur = cur.next;
if (l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummy.next;
}
|
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(max(m, n)),反转链表和相加操作都是线性时间。
- 空间复杂度:
O(1),仅使用固定数量的指针。
总结
| 解法 |
时间复杂度 |
空间复杂度 |
优点 |
| 栈辅助法 |
O(max(m, n)) |
O(m + n) |
逻辑清晰,但需要额外栈空间 |
| 链表反转法 |
O(max(m, n)) |
O(1) |
空间更优,但修改了原始链表 |
两种方法各有优劣:
- 栈辅助法:不修改原始链表,逻辑清晰,但需要额外空间存储栈。
- 链表反转法:空间效率更高,但会修改原始链表结构。
在实际应用中,如果原始链表不可修改,应选择栈辅助法;若空间效率是首要考虑因素,则链表反转法更优。两种方法的时间复杂度相同,都能高效解决该问题。
来源
445. 两数相加 II | 力扣(LeetCode)


